D5.4 - Techno-economic validation: Main conclusions and recommendations
This report focused on the evaluation of results and compilation of recommendations for a future gas grid. The report proposes four possible gas grids characterized by H2 content and the need for separation. The key findings are as follows:
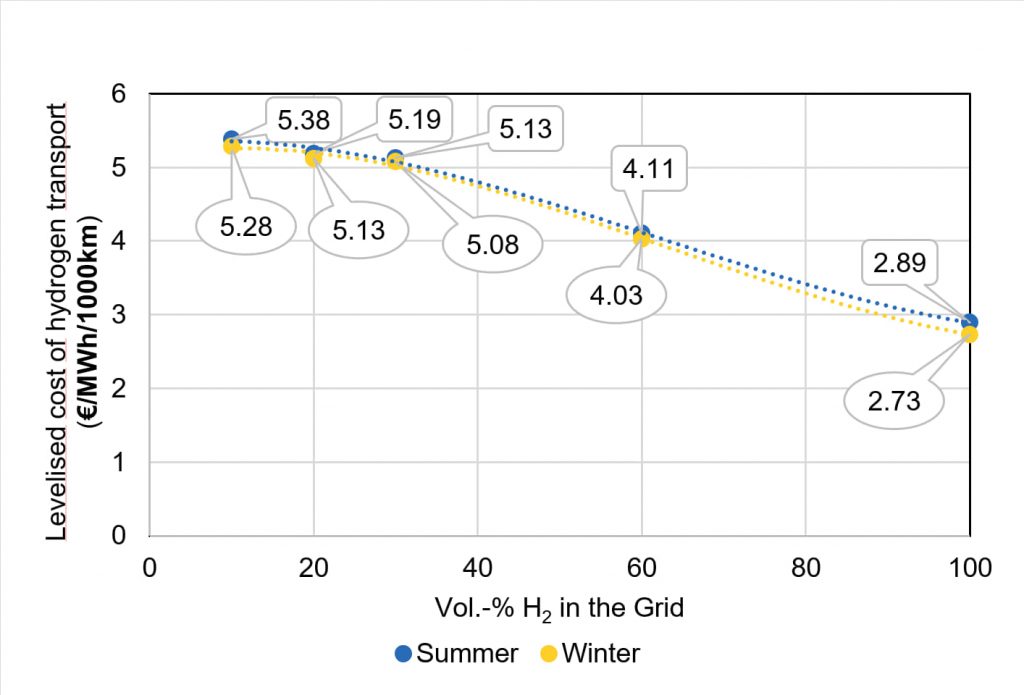
Blending low volumes (0-2 vol.-%) of hydrogen into the existing gas grid facilitates a gradual transition, utilizing the existing infrastructure with minimal modifications.
Retrofitting the existing gas infrastructure allows for blending higher volumes (2-30 vol.-%) of hydrogen, enabling the use of natural gas appliances to a certain degree and minimizing disruption to end-users.
Implementing separation technology at the transmission level (2-30 vol.-% with separation) allows for the utilization of the existing infrastructure while balancing supply and demand of renewable energy sources.
Retrofitting the natural gas grid for 100% hydrogen provides a cost-effective solution for the distribution and storage of hydrogen, promoting energy diversification and decarbonization.
Based on these findings, the report offers several technical and economic recommendations. From a technical standpoint, a compatibility assessment of the existing gas grid infrastructure is advised, along with necessary retrofits and determining the optimal blending ratio. In the long term, retrofitting parts of the grid for 100% hydrogen is recommended. On the economic side, assessing hydrogen supply availability, cost, and reliability, as well as pushing for favorable regulatory environments, are highlighted.
The report concludes that the European gas grid’s future direction will depend on local conditions, but a holistic European solution is needed in the long term. Transporting hydrogen in a retrofitted gas grid is not only economically competitive but also necessary to achieve emission targets. The report’s findings will contribute to the development of hydrogen injection potential scenarios in Europe.